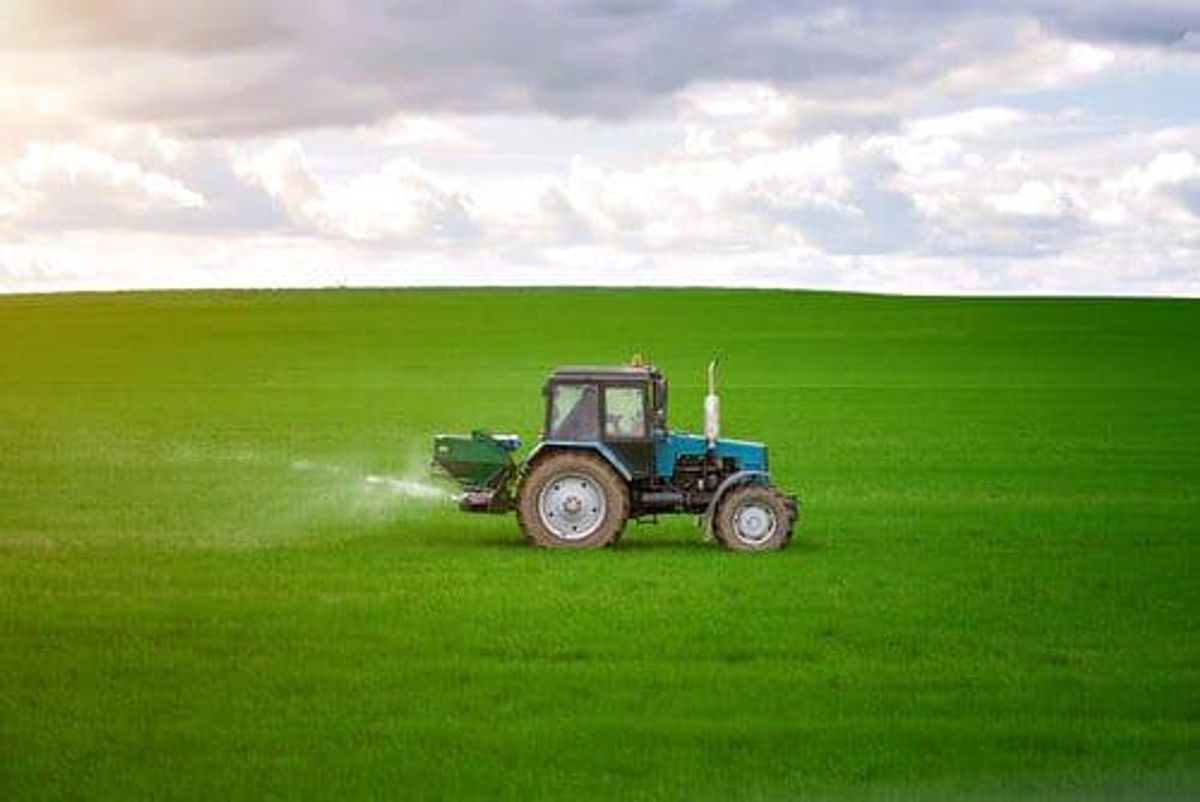
Potash is a potassium-bearing nutrient essential for growing healthy, high-yield crops, and there are four kinds that market participants should have on their radar.
These minerals are found in large evaporate deposits from ancient lakes and sea beds, or in rock formations. The top potash-producing countries include Canada, Belarus and Russia.
For those looking to invest in the potash market, it is important to understand the four deposit forms and the different uses for each variation of the mineral.
Here the Investing News Network provides an overview of the four kinds of potash. These varieties are sylvite, polyhalite, langbeinite and carnallite, with the first three being the largest market segments.
Kinds of potash: Sylvite
If a company ever uses the words “regular potash,” investors should know that it is referring to sylvite, which is the mineral name for potassium chloride (KCl).
Sylvite is the most common form of potash, with massive deposits found in the US. However, the largest-known deposits of sylvite come from Devonian evaporite basins in Saskatchewan, Canada.
KCl is also known as muriate of potash (MOP). MOP is the most commonly used fertilizer, and is particularly helpful for chloride-loving vegetables such as sugar beets, corn, celery and Swiss chard. It can be beneficial for soil that is low in chloride, building the plants’ disease resistance.
MOP accounts for the largest potash market, with production of over 61 million tonnes per year. As far as pricing is concerned, MOP is the standard price that investors see quoted most often.
Nutrien (TSX:NTR,NYSE:NTR) is a major producer of MOP, but rising demand for this kind of potash has also attracted junior exploration companies to the market, including Highfield Resources (ASX:HFR), Western Resources (TSX:WRX) and Gensource Potash (TSXV:GSP).
It’s worth noting that when sylvite is found mixed with sodium chloride, the mineral it creates is called sylvinite. This mineral is a variation of sylvite and is also an important source for potash.
Kinds of potash: Polyhalite
Chloride is toxic to some fruits and vegetables, and in those cases farmers use polyhalite instead of MOP. Polyhalite is a potash mineral that contains the key nutrients potassium and sulfur.
Polyhalite is known to the market as sulfate of potash (SOP), and is the second most commonly used form of potash. Global annual production of SOP comes in at roughly 6 million tonnes.
SOP makes plants more resilient to drought, frost, insects and even disease, which in turn improves plant quality and crop yields. SOP can also improve the look and taste of foods and can improve a plant’s ability to absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and iron.
SOP is not a naturally occurring mineral, and usually must be produced through chemical methods, such as those used by Kalium Lakes (ASX:KLL). Because of the resource-intensive processes used to create it, SOP fetches a significant premium over MOP.
There are a few companies that can manufacture SOP with naturally occurring brine salts, including Compass Minerals International (NYSE:CMP) and SQM (NYSE:SQM).
Smaller fertilizer companies looking to produce SOP include Agrimin (ASX:AMN), Danakali (ASX:DNK,OTC Pink:SBMSF) and Reward Minerals (ASX:RWD). Australian Potash (ASX:APC) has updated its flow modelling outlines with potential for increased production from brine at the Lake Wells Sulphate of Potash project.
Kinds of potash: Langbeinite
Langbeinite is a potassium magnesium form of potash; however, it also contains sulfate, giving it the name sulfate of potash magnesia (SOPM).
Similar to SOP, this variation of potash is used for chloride-sensitive fruit and vegetable crops, but particularly where there is a magnesium deficiency in the soil. SOPM is primarily a magnesium fertilizer, so it is a niche market within the larger the industry.
There few langbeinite producers; Intrepid Potash (NYSE:IPI) is the only SOPM producer in the US.
Kinds of potash: Carnallite
Once the go-to form of potash, carnallite is made up of potassium chloride, magnesium and water. However, these compounded minerals make it a tricky mineral from which to extract potash fertilizer. As a result, it is a good type of potash to use only when there is no source of sylvite or sylvinite.
Carnallite is mined for both its potash and magnesium properties.
The global distribution of this mineral is fairly vast, with occurrences in the Four Corners region of the US, including New Mexico and Utah’s Paradox Basin, as well as Colorado. It is also found in Russia, Canada, Germany and in some regions in the Middle East. Companies with carnallite projects include Kore Potash (LSE:KP2), and Karnalyte Resources (TSX:KRN).
This is an updated version of an article first published by the Investing News Network in 2013.
Don’t forget to follow us @INN_Resource for real-time updates!
Securities Disclosure: I, Melissa Pistilli, hold no direct investment interest in any company mentioned in this article.
Source
Source: https://hempland.net/4-kinds-of-potash-sylvite-polyhalite-langbeinite-and-carnallite/