The cannabis plant contains at least 120 naturally-occurring cannabinoids that can cause physiological reactions in the mammalian body. Two cannabinoids typically attract the most attention: CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). These chemical compounds can be extracted from the cannabis plant and ingested to provide benefits to mammalian health and wellbeing. However, the physiological effects of CBD and THC differ somewhat. While both cannabinoids can help treat a number of physical and mental conditions such as chronic pain, inflammation and anxiety, one fundamental difference is that CBD is non-psychotropic and does not elicit a high, whereas THC has intoxicating effects.
In addition to the presence of psychotropic effects, CBD and THC display several differences in terms of structure, side effects and legality, as well as some key similarities. In this article, we’ll take a look at how the most notable cannabinoids compare.
CBD vs THC
|
|
CBD |
THC |
|
Source |
Hemp and marijuana, but typically sourced from hemp due to its low THC content |
Marijuana |
|
Legal in the UK |
✅ |
❌ |
|
Psychoactive |
❌ |
✅ |
|
Side Effects |
Rare |
Psychoactive |
|
May trigger a positive drug test result |
Unlikely |
✅ |
|
Interacts with the ECS |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Relieves pain & inflammation |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Relieves stress & anxiety |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Improves sleep |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Appetite Stimulant |
❌ |
✅ |
Sources
CBD and THC are both naturally-occurring chemical compounds (cannabinoids) of the cannabis plant. The cannabis plant family, however, covers many different species, each of which contains varying levels of cannabinoids. Hemp is a specific variety of the Cannabis sativa plant and it is rich in CBD with low levels of THC. Other Cannabis sativa plants contain higher levels of THC and lower quantities of CBD.
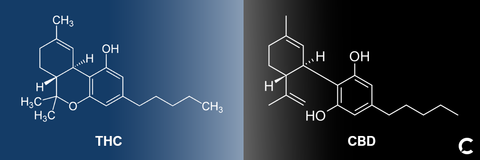
Chemical Structure
In terms of molecular formula, CBD and THC are the same (C21H30O2), consisting of twenty-one carbon atoms, thirty hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. However, the atoms are arranged within a different structure which provides CBD and THC with distinct chemical properties. This means that while both CBD and THC work with receptors of the endocannabinoid system, they ultimately affect the body in different ways.
Physiological Effects
Both CBD and THC stimulate the CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system, which control mood, sleep, pain, appetite, metabolism and more. Both CBD and THC can provide several benefits to physiology by doing this, including reducing pain and inflammation, promoting relaxation and sleep, easing anxiety and stress, etc. However, THC also causes a euphoric feeling due to its psychoactive properties. CBD, on the other hand, can provide many similar wellness benefits without inducing feelings of euphoria. THC can also significantly boost appetite (you may have heard of the infamous “munchies”), whereas CBD seems to have little or no effect on appetite.
Medical Uses
Some research indicates that CBD can be useful for:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Chronic pain
- Arthritis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Nausea
- Glaucoma
- Migraine
- Parkinson’s disease tremors
In the UK, NICE has recommended one CBD-based drug for use in the NHS. Epidyolex contains pure CBD and is endorsed as a treatment for two severe and complex forms of epilepsy, Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
In some countries and states where medicinal marijuana is legal, THC may be used for:
- Nerve pain
- Nausea
- Glaucoma
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson’s diseases tremors
- Low appetite
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
How to Take
Both CBD and THC can be consumed in a variety of forms. THC is often consumed as marijuana via smoking but is present in some oils, tinctures and vaporiser products. CBD is commonly taken sublingually as an oil. Dropping the oil under the tongue and holding it there for 60 seconds enables cannabidiol to quickly enter the bloodstream. CBD can also be infused into edibles, gummies and beverages, and topical products such as balms, salves and creams which are applied to the skin as required to deliver localised benefits.
Side Effects
Side effects from CBD are uncommon, but may include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Low blood pressure
Side effects associated with THC include:
- Drowsiness
- Sickness
- Memory loss
- Problems focusing
UK Legislation
CBD is legal in the UK, as long as it contains no more than 0.2% THC. This is always worth checking when purchasing a CBD-based product; THC content is usually made clear on the packaging and a reputable manufacturer will be happy to provide independent third-party lab reports to clarify. By contrast, THC, for non-medical purposes, remains illegal.
The Bottom Line
Cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the two most prominent cannabinoids found in cannabis. THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the “high” that people experience when they use marijuana. CBD, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and does not produce any psychoactive effects. This is the main difference between CBD and THC.
Additionally, CBD is legal in the UK, if it does not contain more than 0.2% THC. THC (or marijuana) is still classified as an illegal drug.
CBD and THC do share some similarities. They share the same molecular formula, for instance, but a marginally altered arrangement of atoms. This minute difference in atom arrangement results in each compound having different effects on the human body. For instance, THC is regarded as an appetite stimulant, whereby CBD is not.
Source: https://www.missionc.com/blogs/news/cbd-vs-thc-whats-the-difference





